e-Way Bill – Everything You Need to Know
As per the latest data, e-way bills hit a record high of over 84 million in September, highlighting their increasing significance in Indian industries. The main objective of e-Way bills is to streamline the movement of goods by reducing transit time, minimizing paperwork, and enhancing transparency in the ecosystem.
In this blog, we will delve deeper into e-Way bills, their applicability, and the penalties for non-compliance.
What Is an e-Way Bill?
The Electronic Way Bill, commonly known as the e-Way Bill, is an essential document for moving goods. As per the GST regulations, any GST-registered individual cannot transport goods in a vehicle whose value exceeds ₹50,000 (single invoice/bill/delivery challan) without an e-Way bill generated from the official e-Way bill portal, which can be accessed at ewaybillgst.gov.in.
Generating and canceling e-Way bills have been convenient through multiple modes, including SMS, Android App, and API site-to-site integration. Upon generation of an e-Way bill, a unique e-Way Bill Number (EBN) is assigned, which can be accessed by the supplier, recipient, and transporter involved in the transaction.
When Is an e-Way Bill Generated?
e-Way bills are generated in the following situations:
Transactions of More Than ₹50,000
If you're moving goods worth more than ₹50,000 via a vehicle or conveyance, you must generate an e-Way bill. This applies to various situations, including when you're making a 'supply' or even when you're making a return.
A 'supply' can take many forms, such as a sale or a transfer of goods. And whether or not payment is involved, the value of the goods being moved determines whether you need to generate an e-Way bill.
Transactions Less Than ₹50,000
It is mandatory to generate an e-Way bill even if the value of the goods transported is less than ₹50,000. But this applies to certain specified goods and situations, such as:
If a principal or a registered job worker is moving goods interstate, the e-Way bill must be generated regardless of the value of the consignment.
For dealers exempted from GST registration who are transporting handicraft goods interstate, the e-Way bill is mandatory, irrespective of the value of the consignment.
Failing to comply with these rules can result in penalties and even confiscation and seizure of the goods being transported. Therefore, ensure that the e-Way bill is generated in a timely and accurate manner for all applicable consignments, regardless of their value.
Penalty for Violation of e-Way Bill Rules
Defaulters of GST e-Way rules can face penalties according to Indian government norms:
As per Section 122 of CGST Act, 2017, a taxable person transporting taxable goods without specified documents (including an e-Way bill) can face a penalty of ₹10,000/- or the tax sought to be evaded (whichever is greater)
Goods not listed in a GST e-Way bill and found being transported or stored can be subject to detention or seizure under Section 129 of CGST Act, 2017
Incorrect or Fake e-Way Bill:
Penalties for generating incorrect or fake e-Way bills:
Spelling mistakes in the name of the consignor or consignee are allowed as long as the relevant GSTIN is included in the e-Way bill, tax invoice, or related documents.
Errors in the Pin-code are allowed if the address of the consignor or consignee matches the relevant information. However, the error in the Pin-code should not affect the validity period of the e-Way bill.
Errors in the address of the consignor or consignee are allowed if the address mentioned in the documents is close to the locality of the recipient of the goods, provided that all other details related to the goods are correctly mentioned.
One or two-digit mistakes in the document number mentioned in the e-Way bill, tax invoice, or related documents are allowed. However, if there are multiple mistakes related to the document number, the benefits of the Circular become ineffective.
Errors in the 4 or 6-digit level of HSN codes are allowed if the first two digits of the HSN codes are relevant to the goods transported, the concerned individual paid the tax, and it was mentioned correctly in the e-Way bill. In this case, the penalty as per Section 129 of the CGST Act is ineffective.
Errors in mentioning the vehicle number are allowed if the error extends only up to two digits or characters of the allotted vehicle number. In such cases, the penalty shall not apply.
According to the Circular, if an authorized officer finds these errors, a penalty of ₹500 will be levied as per Section 125 of the CGST Act and ₹500 as per the respective state GST Act. This means that a total of ₹1000 will need to be paid for each consignment in question. The individual responsible for the goods or the transporter must pay the penalty by submitting Form GST DRC-07.
Moreover, all penalties issued under Section 125 of the CGST Act will be documented by the enforcing officer, who will also explain the reason for not implementing Section 129 of the CGST Act to the controlling officer weekly.
Transporting Goods without Valid Documents in E-Way Bills
As per the GST Act and the rules, every transporter and supplier must carry valid documents related to the goods during transit. In case of any violation, the concerned officers may detain or seize the goods, which can cause significant disruptions in the transportation process.
To avoid such penalties, the supplier or transporter should ensure compliance with the e-Way bill rules. In case of any violation, the person shall make the payment for a penalty as per Section 129(1) clause (a) and clause (b) of the CGST Act.
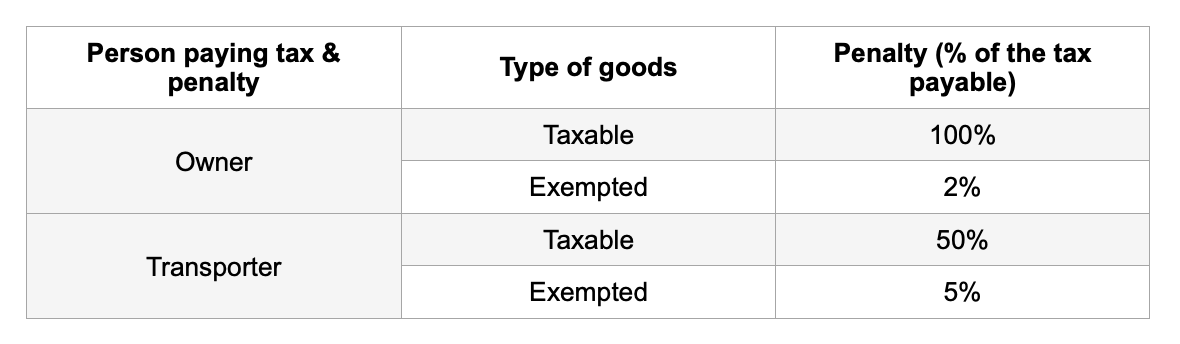
Let's take a closer look at the penalty amount and conditions for different scenarios:
Without paying Tax and valid documents
If the supplier or transporter fails to pay taxes and transport goods without valid documents, the concerned individual shall pay the applicable tax and penalty equal to 100% of the total tax payable on the value of the goods transported.
If the person transported exempted goods, the person should pay the amount equal to two percent of the value of the goods, or the individual shall pay a penalty of Rs.25,000, whichever is less in the penalty payment.
Only without valid documents
If the supplier or transporter paid the tax for the goods but transported without valid documents, the individual shall make a payment equal to 50% of the total value of the goods carried.
If the concerned individual transported exempted goods, the person should pay the amount equal to five percent of the value of the goods, or the individual should pay a penalty of Rs.25,000, whichever is less in the penalty payment.
In case of any seizure or detention of goods, the officers shall release the seized or detained goods or the stored when the supplier or the transporter satisfies the abovementioned conditions.
Release of Seized Goods
If a taxpayer fails to comply with the e-Way bill rules, it can result in both monetary and non-monetary losses. Let's look at the monetary penalties associated with e-Way bill violations.
According to section 122(1) of the Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST) Act, 2017, any movement of goods without a valid e-Way bill constitutes an offense and is subject to a penalty of either ₹10,000 or the amount of tax sought to be evaded (whichever is greater).
Additionally, as per the provisions of section 129 of the CGST Act, any vehicle transporting goods without a valid e-Way bill can be detained or seized by an officer. The detained or seized vehicle will only be released after the payment of appropriate taxes and penalties.
If goods are seized, they can be released in one of two ways. The first option is to pay the penalty, which is either the amount of tax sought to be evaded or ₹25,000 (whichever is lesser) plus the tax payable. The second option is to provide a bond along with security in the form of a bank guarantee equal to the total amount due
Non-compliance with e-Way bill rules can result in significant financial losses. Therefore, taxpayers must ensure they generate an e-Way bill when required and comply with all e-Way bill provisions to avoid penalties or seizures.
Note that failure to pay the appropriate taxes and penalties within seven days can lead to legal action being taken against the owner or transporter. In such a scenario, both the vehicle and the goods can be detained until the matter is resolved.
It's crucial to comply with the regulations and ensure that all taxes and penalties are paid on time to avoid any legal complications.
Stay Safe of Hefty Penalties
Our company understands the importance of compliance and timely generation of e-Way bills to avoid penalties and legal complications. With our expert services, you can be assured that your e-Way bills will be generated accurately and on time, saving you from unnecessary penalties.
Don't let compliance issues and penalties burden you any longer. Contact us today to learn more about our services and how we can help you.